 react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view
react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view
A ScrollView component that handles keyboard appearance and automatically scrolls to focused TextInput.
Top Related Projects
React Native's Animated library reimplemented
Declarative API exposing platform native touch and gesture system to React Native.
An enhanced, animated, customizable Modal for React Native.
React Native Network Info API for Android & iOS
An asynchronous, persistent, key-value storage system for React Native.
Quick Overview
APSL/react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view is a React Native component that automatically adjusts its height, position, or bottom padding based on whether the keyboard is visible. This library aims to solve the common issue of the keyboard obscuring input fields in scrollable views, providing a seamless user experience for forms and text input in mobile applications.
Pros
- Easy to implement and integrate into existing React Native projects
- Automatically handles keyboard appearance and disappearance
- Supports both iOS and Android platforms
- Customizable behavior through various props
Cons
- May have performance issues with large, complex views
- Some users report occasional glitches or unexpected behavior
- Limited documentation for advanced use cases
- Requires manual updates to keep up with React Native version changes
Code Examples
- Basic usage with a ScrollView:
import { KeyboardAwareScrollView } from 'react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view';
const MyComponent = () => (
<KeyboardAwareScrollView>
<TextInput placeholder="Enter text here" />
{/* Other components */}
</KeyboardAwareScrollView>
);
- Using with a FlatList:
import { KeyboardAwareFlatList } from 'react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view';
const MyList = () => (
<KeyboardAwareFlatList
data={myData}
renderItem={({ item }) => <ListItem item={item} />}
keyExtractor={(item) => item.id}
/>
);
- Customizing behavior with props:
<KeyboardAwareScrollView
enableOnAndroid={true}
enableAutomaticScroll={true}
extraHeight={120}
extraScrollHeight={20}
keyboardOpeningTime={0}
>
{/* Your content */}
</KeyboardAwareScrollView>
Getting Started
-
Install the package:
npm install react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view -
Import and use the component in your React Native app:
import { KeyboardAwareScrollView } from 'react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view'; const App = () => ( <KeyboardAwareScrollView> <TextInput placeholder="Username" /> <TextInput placeholder="Password" secureTextEntry /> <Button title="Submit" onPress={handleSubmit} /> </KeyboardAwareScrollView> ); -
Customize the component behavior using props as needed for your specific use case.
Competitor Comparisons
React Native's Animated library reimplemented
Pros of react-native-reanimated
- Offers advanced animation capabilities with a declarative API
- Provides better performance by running animations on the native thread
- Supports complex gestures and interactions
Cons of react-native-reanimated
- Steeper learning curve due to its more complex API
- Requires additional setup and configuration
- May be overkill for simple keyboard-aware scrolling needs
Code Comparison
react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view:
import { KeyboardAwareScrollView } from 'react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view';
<KeyboardAwareScrollView>
{/* Your content here */}
</KeyboardAwareScrollView>
react-native-reanimated:
import Animated from 'react-native-reanimated';
const animatedStyle = useAnimatedStyle(() => {
return { transform: [{ translateY: scrollY.value }] };
});
<Animated.ScrollView style={animatedStyle}>
{/* Your content here */}
</Animated.ScrollView>
react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view is simpler to use and focuses specifically on keyboard-aware scrolling. It's ideal for basic keyboard avoidance scenarios. react-native-reanimated, on the other hand, is a more powerful and versatile animation library that can handle complex animations and interactions, including keyboard-aware scrolling. However, it requires more setup and has a steeper learning curve. Choose based on your project's specific needs and complexity requirements.
Declarative API exposing platform native touch and gesture system to React Native.
Pros of react-native-gesture-handler
- Provides a more comprehensive gesture handling system for React Native
- Offers better performance and smoother animations
- Supports a wider range of gestures and interactions
Cons of react-native-gesture-handler
- Has a steeper learning curve due to its more complex API
- Requires more setup and configuration compared to simpler solutions
- May be overkill for basic keyboard avoidance needs
Code Comparison
react-native-gesture-handler:
import { PanGestureHandler } from 'react-native-gesture-handler';
<PanGestureHandler
onGestureEvent={this._onPanGestureEvent}
onHandlerStateChange={this._onPanHandlerStateChange}>
<Animated.View style={animatedStyles} />
</PanGestureHandler>
react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view:
import { KeyboardAwareScrollView } from 'react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view';
<KeyboardAwareScrollView>
<View style={styles.container}>
{/* Your content here */}
</View>
</KeyboardAwareScrollView>
While react-native-gesture-handler provides powerful gesture handling capabilities, react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view offers a simpler solution specifically for keyboard-aware scrolling. The choice between the two depends on the project's requirements and complexity.
An enhanced, animated, customizable Modal for React Native.
Pros of react-native-modal
- Specifically designed for creating modals, offering a wide range of customization options
- Supports animations and gestures out of the box
- Handles device orientation changes and provides a consistent experience across platforms
Cons of react-native-modal
- Limited to modal functionality, not suitable for general scrolling or keyboard avoidance
- May require additional setup for complex layouts or nested scrollable content
- Potential performance impact when using heavy animations or multiple modals
Code Comparison
react-native-modal:
<Modal isVisible={isModalVisible} onBackdropPress={() => setModalVisible(false)}>
<View style={styles.modalContent}>
<Text>Modal Content</Text>
<Button title="Close" onPress={() => setModalVisible(false)} />
</View>
</Modal>
react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view:
<KeyboardAwareScrollView>
<View style={styles.content}>
<TextInput placeholder="Enter text" />
<Button title="Submit" onPress={handleSubmit} />
</View>
</KeyboardAwareScrollView>
While react-native-modal focuses on creating customizable modal overlays, react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view is designed to handle keyboard interactions and scrolling. The choice between these libraries depends on the specific requirements of your project, such as whether you need modal functionality or keyboard-aware scrolling.
React Native Network Info API for Android & iOS
Pros of react-native-netinfo
- Focuses on network connectivity information, providing detailed network state and type
- Offers cross-platform support for iOS, Android, Windows, macOS, and Web
- Provides real-time network change detection and event listeners
Cons of react-native-netinfo
- Limited to network-related functionality, not addressing keyboard-aware scrolling
- May require additional setup for certain platforms or configurations
- Doesn't handle UI adjustments for keyboard appearance
Code Comparison
react-native-netinfo:
import NetInfo from "@react-native-community/netinfo";
NetInfo.fetch().then(state => {
console.log("Connection type", state.type);
console.log("Is connected?", state.isConnected);
});
react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view:
import { KeyboardAwareScrollView } from 'react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view';
<KeyboardAwareScrollView>
<View>
<TextInput />
</View>
</KeyboardAwareScrollView>
Summary
react-native-netinfo and react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view serve different purposes. The former focuses on network connectivity information and management, while the latter addresses keyboard-aware scrolling in React Native applications. react-native-netinfo is ideal for apps requiring network state monitoring, whereas react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view is better suited for improving user experience with forms and text input on mobile devices.
An asynchronous, persistent, key-value storage system for React Native.
Pros of async-storage
- Provides a simple, asynchronous, persistent key-value storage system
- Widely adopted and maintained by the React Native community
- Supports multiple storage backends (SQLite, RocksDB, LevelDB)
Cons of async-storage
- Limited to key-value storage, not suitable for complex data structures
- Doesn't handle keyboard-related UI adjustments
- May require additional setup for certain platforms or storage backends
Code Comparison
react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view:
import { KeyboardAwareScrollView } from 'react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view';
<KeyboardAwareScrollView>
<TextInput />
</KeyboardAwareScrollView>
async-storage:
import AsyncStorage from '@react-native-async-storage/async-storage';
await AsyncStorage.setItem('key', 'value');
const value = await AsyncStorage.getItem('key');
The two libraries serve different purposes. react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view focuses on improving the user experience by adjusting the scroll view when the keyboard appears, while async-storage provides a simple storage solution for persisting data in React Native applications. The choice between them depends on the specific needs of your project, whether it's handling keyboard interactions or managing data storage.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view


A ScrollView component that handles keyboard appearance and automatically scrolls to focused TextInput.
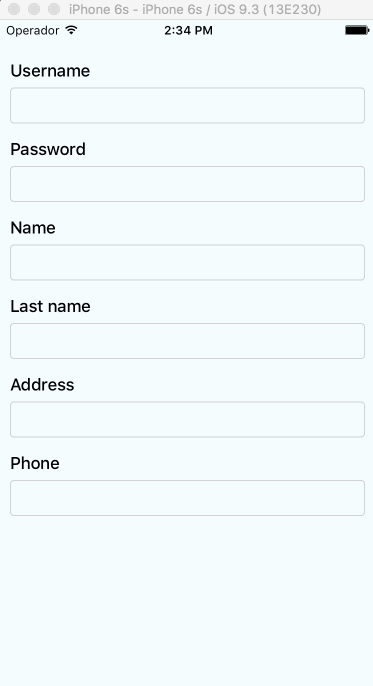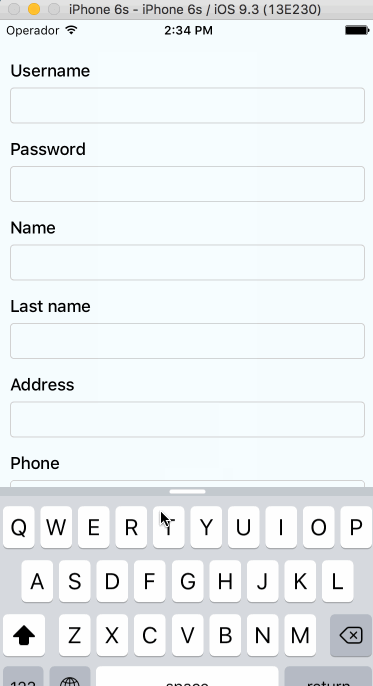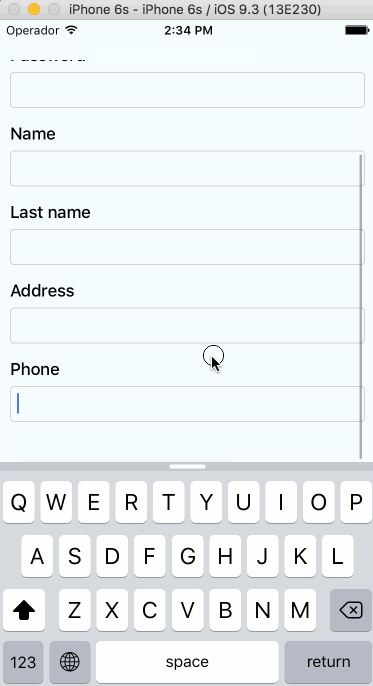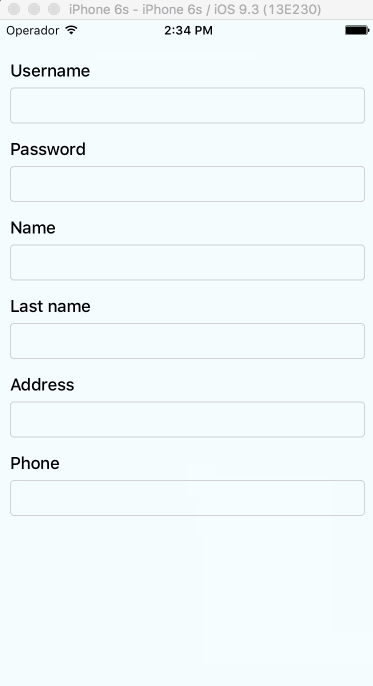
Supported versions
v0.4.0requiresRN>=0.48v0.2.0requiresRN>=0.32.0.v0.1.2requiresRN>=0.27.2but you should use0.2.0in order to make it work with multiple scroll views.v0.0.7requiresreact-native>=0.25.0.- Use
v0.0.6for older RN versions.
Installation
Installation can be done through npm or yarn:
npm i react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view --save
yarn add react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view
Usage
You can use the KeyboardAwareScrollView, KeyboardAwareSectionList or the KeyboardAwareFlatList
components. They accept ScrollView, SectionList and FlatList default props respectively and
implement a custom high order component called KeyboardAwareHOC to handle keyboard appearance.
The high order component is also available if you want to use it in any other component.
Import react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view and wrap your content inside
it:
import { KeyboardAwareScrollView } from 'react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view'
<KeyboardAwareScrollView>
<View>
<TextInput />
</View>
</KeyboardAwareScrollView>
Auto-scroll in TextInput fields
As of v0.1.0, the component auto scrolls to the focused TextInput ð. For versions v0.0.7 and older you can do the following.
Programatically scroll to any TextInput
In order to scroll to any TextInput field, you can use the built-in method scrollToFocusedInput. Example:
_scrollToInput (reactNode: any) {
// Add a 'scroll' ref to your ScrollView
this.scroll.props.scrollToFocusedInput(reactNode)
}
<KeyboardAwareScrollView
innerRef={ref => {
this.scroll = ref
}}>
<View>
<TextInput
onFocus={(event: Event) => {
// `bind` the function if you're using ES6 classes
this._scrollToInput(ReactNative.findNodeHandle(event.target))
}}
/>
</View>
</KeyboardAwareScrollView>
Programatically scroll to any position
There's another built-in function that lets you programatically scroll to any position of the scroll view:
this.scroll.props.scrollToPosition(0, 0)
Register to keyboard events
You can register to ScrollViewResponder events onKeyboardWillShow and onKeyboardWillHide:
<KeyboardAwareScrollView
onKeyboardWillShow={(frames: Object) => {
console.log('Keyboard event', frames)
}}>
<View>
<TextInput />
</View>
</KeyboardAwareScrollView>
Android Support
First, Android natively has this feature, you can easily enable it by setting windowSoftInputMode in AndroidManifest.xml. Check here.
But if you want to use feature like extraHeight, you need to enable Android Support with the following steps:
- Make sure you are using react-native
0.46or above. - Set
windowSoftInputModetoadjustPaninAndroidManifest.xml. - Set
enableOnAndroidproperty totrue.
Android Support is not perfect, here is the supported list:
| Prop | Android Support |
|---|---|
viewIsInsideTabBar | Yes |
resetScrollToCoords | Yes |
enableAutomaticScroll | Yes |
extraHeight | Yes |
extraScrollHeight | Yes |
enableResetScrollToCoords | Yes |
keyboardOpeningTime | No |
API
Props
All the ScrollView/FlatList props will be passed.
| Prop | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
innerRef | Function | Catch the reference of the component. |
viewIsInsideTabBar | boolean | Adds an extra offset that represents the TabBarIOS height. |
resetScrollToCoords | Object: {x: number, y: number} | Coordinates that will be used to reset the scroll when the keyboard hides. |
enableAutomaticScroll | boolean | When focus in TextInput will scroll the position, default is enabled. |
extraHeight | number | Adds an extra offset when focusing the TextInputs. |
extraScrollHeight | number | Adds an extra offset to the keyboard. Useful if you want to stick elements above the keyboard. |
enableResetScrollToCoords | boolean | Lets the user enable or disable automatic resetScrollToCoords. |
keyboardOpeningTime | number | Sets the delay time before scrolling to new position, default is 250 |
enableOnAndroid | boolean | Enable Android Support |
Methods
Use innerRef to get the component reference and use this.scrollRef.props to access these methods.
| Method | Parameter | Description |
|---|---|---|
getScrollResponder | void | Get ScrollResponder |
scrollToPosition | x: number, y: number, animated: bool = true | Scroll to specific position with or without animation. |
scrollToEnd | animated?: bool = true | Scroll to end with or without animation. |
scrollIntoView | element: React.Element<*>, options: { getScrollPosition: ?(parentLayout, childLayout, contentOffset) => { x: number, y: number, animated: boolean } } | Scrolls an element inside a KeyboardAwareScrollView into view. |
Using high order component
Enabling any component to be keyboard-aware is very easy. Take a look at the code of KeyboardAwareFlatList:
/* @flow */
import { FlatList } from 'react-native'
import listenToKeyboardEvents from './KeyboardAwareHOC'
export default listenToKeyboardEvents(FlatList)
The HOC can also be configured. Sometimes it's more convenient to provide a static config than configuring the behavior with props. This HOC config can be overriden with props.
/* @flow */
import { FlatList } from 'react-native'
import listenToKeyboardEvents from './KeyboardAwareHOC'
const config = {
enableOnAndroid: true,
enableAutomaticScroll: true
}
export default listenToKeyboardEvents(config)(FlatList)
The available config options are:
{
enableOnAndroid: boolean,
contentContainerStyle: ?Object,
enableAutomaticScroll: boolean,
extraHeight: number,
extraScrollHeight: number,
enableResetScrollToCoords: boolean,
keyboardOpeningTime: number,
viewIsInsideTabBar: boolean,
refPropName: string,
extractNativeRef: Function
}
License
MIT.
Author
Ãlvaro Medina Ballester <amedina at apsl.net>
Built with ð by APSL.
Top Related Projects
React Native's Animated library reimplemented
Declarative API exposing platform native touch and gesture system to React Native.
An enhanced, animated, customizable Modal for React Native.
React Native Network Info API for Android & iOS
An asynchronous, persistent, key-value storage system for React Native.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot