 bignumber.js
bignumber.js
A JavaScript library for arbitrary-precision decimal and non-decimal arithmetic
Top Related Projects
An extensive math library for JavaScript and Node.js
An arbitrary length integer library for Javascript
BigNum in pure javascript
Quick Overview
BigNumber.js is a JavaScript library for arbitrary-precision decimal and non-decimal arithmetic. It provides a way to perform calculations with numbers of any size and precision, overcoming the limitations of JavaScript's native number type.
Pros
- Supports arbitrary-precision arithmetic for both decimal and non-decimal numbers
- Comprehensive API with methods for common mathematical operations
- Configurable rounding modes and exponential notation
- Well-documented and actively maintained
Cons
- Performance can be slower compared to native JavaScript operations for simple calculations
- Increased bundle size when including the library in web projects
- Learning curve for developers unfamiliar with arbitrary-precision arithmetic concepts
Code Examples
Creating and performing operations with BigNumber:
const BigNumber = require('bignumber.js');
const a = new BigNumber('0.1');
const b = new BigNumber('0.2');
const sum = a.plus(b);
console.log(sum.toString()); // '0.3'
Handling very large numbers:
const largeNumber = new BigNumber('1e+1000');
const result = largeNumber.times(2).dividedBy(3);
console.log(result.toExponential()); // '6.666666666666667e+999'
Configuring decimal places and rounding:
BigNumber.config({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 4, ROUNDING_MODE: BigNumber.ROUND_HALF_UP });
const x = new BigNumber('1.23456789');
console.log(x.toFixed()); // '1.2346'
Getting Started
To use BigNumber.js in your project:
-
Install the library:
npm install bignumber.js -
Import and use in your JavaScript code:
const BigNumber = require('bignumber.js'); const num = new BigNumber('123.456789'); console.log(num.toFixed(2)); // '123.46'
For browser usage, include the script in your HTML:
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/bignumber.js/9.1.1/bignumber.min.js"></script>
Then use it in your JavaScript:
const num = new BigNumber('9876543210');
console.log(num.plus(1).toString()); // '9876543211'
Competitor Comparisons
An extensive math library for JavaScript and Node.js
Pros of mathjs
- Comprehensive mathematical library with a wide range of functions
- Supports complex numbers, matrices, and units
- Provides a flexible expression parser and evaluator
Cons of mathjs
- Larger file size and potentially slower performance for basic operations
- Steeper learning curve due to its extensive feature set
- May be overkill for projects that only require basic arithmetic
Code Comparison
mathjs:
import { create, all } from 'mathjs'
const math = create(all)
const result = math.evaluate('2 + 3 * 4')
console.log(result) // 14
bignumber.js:
import BigNumber from 'bignumber.js'
const result = new BigNumber(2).plus(new BigNumber(3).times(4))
console.log(result.toString()) // 14
Summary
mathjs is a comprehensive mathematical library offering a wide range of functions, including support for complex numbers, matrices, and units. It also provides a flexible expression parser and evaluator. However, it has a larger file size and may have slower performance for basic operations compared to bignumber.js. mathjs has a steeper learning curve due to its extensive feature set and may be overkill for projects that only require basic arithmetic.
bignumber.js, on the other hand, is more focused on arbitrary-precision decimal and non-decimal arithmetic. It's lighter and potentially faster for basic operations but lacks the advanced features and expression parsing capabilities of mathjs.
An arbitrary length integer library for Javascript
Pros of BigInteger.js
- Specialized for integer operations, potentially offering better performance for specific use cases
- Supports additional mathematical operations like modular exponentiation and GCD
- Smaller file size, which may be beneficial for projects with strict size constraints
Cons of BigInteger.js
- Limited to integer operations, lacking support for decimal numbers
- Less actively maintained, with fewer recent updates and contributions
- Smaller community and ecosystem compared to bignumber.js
Code Comparison
BigInteger.js:
var a = BigInteger("123456789");
var b = BigInteger("987654321");
var sum = a.add(b);
var product = a.multiply(b);
bignumber.js:
var a = new BigNumber("123456789");
var b = new BigNumber("987654321");
var sum = a.plus(b);
var product = a.times(b);
Both libraries offer similar syntax for basic arithmetic operations, but bignumber.js provides more extensive features for handling decimal numbers and advanced mathematical operations. BigInteger.js focuses solely on integer arithmetic, which may be sufficient for specific use cases but lacks the versatility of bignumber.js.
BigNum in pure javascript
Pros of bn.js
- Faster performance for large number operations
- Designed specifically for cryptography applications
- Supports more low-level operations
Cons of bn.js
- Less user-friendly API compared to bignumber.js
- Fewer features for general-purpose arithmetic
- Limited documentation and examples
Code Comparison
bn.js:
const BN = require('bn.js');
const a = new BN('1234567890123456789012345678901234567890');
const b = new BN('9876543210987654321098765432109876543210');
const result = a.mul(b);
bignumber.js:
const BigNumber = require('bignumber.js');
const a = new BigNumber('1234567890123456789012345678901234567890');
const b = new BigNumber('9876543210987654321098765432109876543210');
const result = a.times(b);
Both libraries provide similar functionality for handling large numbers, but bn.js is more focused on cryptographic operations and low-level performance, while bignumber.js offers a more user-friendly API for general-purpose arithmetic. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of your project, such as performance needs, ease of use, and the types of operations you'll be performing.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
A JavaScript library for arbitrary-precision decimal and non-decimal arithmetic.
Features
- Integers and decimals
- Simple API but full-featured
- Faster, smaller, and perhaps easier to use than JavaScript versions of Java's BigDecimal
- 8 KB minified and gzipped
- Replicates the
toExponential,toFixed,toPrecisionandtoStringmethods of JavaScript's Number type - Includes a
toFractionand a correctly-roundedsquareRootmethod - Supports cryptographically-secure pseudo-random number generation
- No dependencies
- Wide platform compatibility: uses JavaScript 1.5 (ECMAScript 3) features only
- Comprehensive documentation and test set
If a smaller and simpler library is required see big.js.
It's less than half the size but only works with decimal numbers and only has half the methods.
It also has fewer configuration options than this library, and does not allow NaN or Infinity.
See also decimal.js, which among other things adds support for non-integer powers, and performs all operations to a specified number of significant digits.
Load
The library is the single JavaScript file bignumber.js or ES module bignumber.mjs.
Browser
<script src='path/to/bignumber.js'></script>
ES module
<script type="module">
import BigNumber from './path/to/bignumber.mjs';
Get a minified version from a CDN:
<script src='https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bignumber.js@9.3.0/bignumber.min.js'></script>
Node.js
npm install bignumber.js
const BigNumber = require('bignumber.js');
ES module
import BigNumber from "bignumber.js";
Deno
// @deno-types="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mikemcl/bignumber.js/v9.3.0/bignumber.d.mts"
import BigNumber from 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mikemcl/bignumber.js/v9.3.0/bignumber.mjs';
// @deno-types="https://unpkg.com/bignumber.js@latest/bignumber.d.mts"
import { BigNumber } from 'https://unpkg.com/bignumber.js@latest/bignumber.mjs';
Use
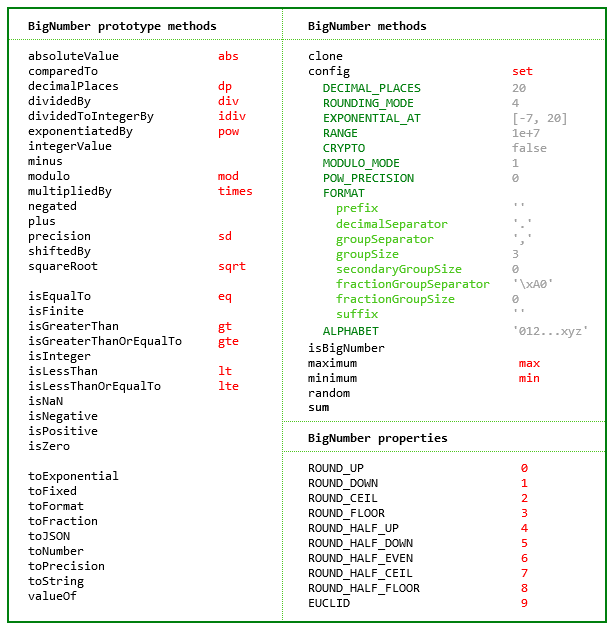
The library exports a single constructor function, BigNumber, which accepts a value of type Number, String or BigNumber,
let x = new BigNumber(123.4567);
let y = BigNumber('123456.7e-3');
let z = new BigNumber(x);
x.isEqualTo(y) && y.isEqualTo(z) && x.isEqualTo(z); // true
To get the string value of a BigNumber use toString() or toFixed(). Using toFixed() prevents exponential notation being returned, no matter how large or small the value.
let x = new BigNumber('1111222233334444555566');
x.toString(); // "1.111222233334444555566e+21"
x.toFixed(); // "1111222233334444555566"
If the limited precision of Number values is not well understood, it is recommended to create BigNumbers from String values rather than Number values to avoid a potential loss of precision.
In all further examples below, let, semicolons and toString calls are not shown. If a commented-out value is in quotes it means toString has been called on the preceding expression.
// Precision loss from using numeric literals with more than 15 significant digits.
new BigNumber(1.0000000000000001) // '1'
new BigNumber(88259496234518.57) // '88259496234518.56'
new BigNumber(99999999999999999999) // '100000000000000000000'
// Precision loss from using numeric literals outside the range of Number values.
new BigNumber(2e+308) // 'Infinity'
new BigNumber(1e-324) // '0'
// Precision loss from the unexpected result of arithmetic with Number values.
new BigNumber(0.7 + 0.1) // '0.7999999999999999'
When creating a BigNumber from a Number, note that a BigNumber is created from a Number's decimal toString() value not from its underlying binary value. If the latter is required, then pass the Number's toString(2) value and specify base 2.
new BigNumber(Number.MAX_VALUE.toString(2), 2)
BigNumbers can be created from values in bases from 2 to 36. See ALPHABET to extend this range.
a = new BigNumber(1011, 2) // "11"
b = new BigNumber('zz.9', 36) // "1295.25"
c = a.plus(b) // "1306.25"
Performance is better if base 10 is NOT specified for decimal values. Only specify base 10 when you want to limit the number of decimal places of the input value to the current DECIMAL_PLACES setting.
A BigNumber is immutable in the sense that it is not changed by its methods.
0.3 - 0.1 // 0.19999999999999998
x = new BigNumber(0.3)
x.minus(0.1) // "0.2"
x // "0.3"
The methods that return a BigNumber can be chained.
x.dividedBy(y).plus(z).times(9)
x.times('1.23456780123456789e+9').plus(9876.5432321).dividedBy('4444562598.111772').integerValue()
Some of the longer method names have a shorter alias.
x.squareRoot().dividedBy(y).exponentiatedBy(3).isEqualTo(x.sqrt().div(y).pow(3)) // true
x.modulo(y).multipliedBy(z).eq(x.mod(y).times(z)) // true
As with JavaScript's Number type, there are toExponential, toFixed and toPrecision methods.
x = new BigNumber(255.5)
x.toExponential(5) // "2.55500e+2"
x.toFixed(5) // "255.50000"
x.toPrecision(5) // "255.50"
x.toNumber() // 255.5
A base can be specified for toString.
Performance is better if base 10 is NOT specified, i.e. use toString() not toString(10). Only specify base 10 when you want to limit the number of decimal places of the string to the current DECIMAL_PLACES setting.
x.toString(16) // "ff.8"
There is a toFormat method which may be useful for internationalisation.
y = new BigNumber('1234567.898765')
y.toFormat(2) // "1,234,567.90"
The maximum number of decimal places of the result of an operation involving division (i.e. a division, square root, base conversion or negative power operation) is set using the set or config method of the BigNumber constructor.
The other arithmetic operations always give the exact result.
BigNumber.set({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 10, ROUNDING_MODE: 4 })
x = new BigNumber(2)
y = new BigNumber(3)
z = x.dividedBy(y) // "0.6666666667"
z.squareRoot() // "0.8164965809"
z.exponentiatedBy(-3) // "3.3749999995"
z.toString(2) // "0.1010101011"
z.multipliedBy(z) // "0.44444444448888888889"
z.multipliedBy(z).decimalPlaces(10) // "0.4444444445"
There is a toFraction method with an optional maximum denominator argument
y = new BigNumber(355)
pi = y.dividedBy(113) // "3.1415929204"
pi.toFraction() // [ "7853982301", "2500000000" ]
pi.toFraction(1000) // [ "355", "113" ]
and isNaN and isFinite methods, as NaN and Infinity are valid BigNumber values.
x = new BigNumber(NaN) // "NaN"
y = new BigNumber(Infinity) // "Infinity"
x.isNaN() && !y.isNaN() && !x.isFinite() && !y.isFinite() // true
The value of a BigNumber is stored in a decimal floating point format in terms of a coefficient, exponent and sign.
x = new BigNumber(-123.456);
x.c // [ 123, 45600000000000 ] coefficient (i.e. significand)
x.e // 2 exponent
x.s // -1 sign
For advanced usage, multiple BigNumber constructors can be created, each with its own independent configuration.
// Set DECIMAL_PLACES for the original BigNumber constructor
BigNumber.set({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 10 })
// Create another BigNumber constructor, optionally passing in a configuration object
BN = BigNumber.clone({ DECIMAL_PLACES: 5 })
x = new BigNumber(1)
y = new BN(1)
x.div(3) // '0.3333333333'
y.div(3) // '0.33333'
To avoid having to call toString or valueOf on a BigNumber to get its value in the Node.js REPL or when using console.log use
BigNumber.prototype[require('util').inspect.custom] = BigNumber.prototype.valueOf;
For further information see the API reference in the doc directory.
Test
The test/modules directory contains the test scripts for each method.
The tests can be run with Node.js or a browser. For Node.js use
npm test
or
node test/test
To test a single method, use, for example
node test/methods/toFraction
For the browser, open test/test.html.
Minify
To minify using, for example, terser
npm install -g terser
terser big.js -c -m -o big.min.js
Licence
The MIT Licence.
See LICENCE.
Top Related Projects
An extensive math library for JavaScript and Node.js
An arbitrary length integer library for Javascript
BigNum in pure javascript
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot
