Top Related Projects
LLM inference in C/C++
Inference Llama 2 in one file of pure C
Python bindings for llama.cpp
Inference code for Llama models
The definitive Web UI for local AI, with powerful features and easy setup.
GPT4All: Run Local LLMs on Any Device. Open-source and available for commercial use.
Quick Overview
The directvt/vtm repository is a collection of tools and utilities for working with Virtual Terminal Managers (VTMs), which are a type of terminal emulator used in various operating systems. The project aims to provide a comprehensive set of tools for managing and interacting with VTMs.
Pros
- Cross-platform Compatibility: The project supports multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
- Extensive Functionality: The project offers a wide range of tools and utilities for managing VTMs, including configuration management, scripting, and monitoring.
- Active Development: The project is actively maintained and regularly updated, ensuring that it stays up-to-date with the latest developments in the VTM ecosystem.
- Open-source: The project is open-source, allowing users to contribute to the codebase and customize the tools to their specific needs.
Cons
- Steep Learning Curve: The project may have a steep learning curve for users who are not familiar with VTMs or terminal emulators in general.
- Limited Documentation: The project's documentation may not be as comprehensive as some users would like, making it difficult for new users to get started.
- Dependency on VTM Implementations: The project's functionality is heavily dependent on the specific VTM implementations used by the target operating system, which may limit its flexibility in certain scenarios.
- Performance Concerns: Depending on the specific use case and the complexity of the VTM configuration, the project's tools may have performance implications that need to be considered.
Code Examples
Since directvt/vtm is a collection of tools and utilities, it does not provide a code library that can be easily demonstrated through code examples. The project's functionality is primarily accessed through command-line interfaces and configuration files.
Getting Started
To get started with directvt/vtm, users can follow these steps:
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/directvt/vtm.git -
Navigate to the project directory:
cd vtm -
Install the required dependencies:
# Depending on your operating system, the installation process may vary # For example, on a Unix-based system, you might use a package manager like apt or yum # On Windows, you might use a tool like Chocolatey or Scoop -
Explore the available tools and utilities:
# List the available commands ./vtm --help # Get more information about a specific command ./vtm <command> --help -
Configure the tools to suit your needs:
# The project's documentation should provide guidance on how to configure the various tools # You may need to modify configuration files, environment variables, or other settings -
Start using the tools:
# Depending on the specific tool or utility you want to use, the command syntax may vary ./vtm <command> <options> -
Contribute to the project (optional):
# If you'd like to contribute to the project, you can follow the guidelines in the project's README # This may involve submitting bug reports, feature requests, or even contributing code changes
Competitor Comparisons
LLM inference in C/C++
Pros of llama.cpp
- Highly optimized for running large language models on consumer hardware
- Supports a wide range of LLMs beyond just LLaMA
- Active community with frequent updates and improvements
Cons of llama.cpp
- Focused primarily on inference, not training or fine-tuning
- May require more technical expertise to set up and use effectively
- Limited built-in tools for text generation and interaction
Code Comparison
llama.cpp:
int main(int argc, char ** argv) {
gpt_params params;
if (gpt_params_parse(argc, argv, params) == false) {
return 1;
}
if (params.seed < 0) {
params.seed = time(NULL);
}
// ... (additional initialization code)
}
vtm:
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
struct vtm_config config = {0};
vtm_config_init(&config);
vtm_config_parse_args(&config, argc, argv);
struct vtm_context *ctx = vtm_init(&config);
// ... (additional initialization code)
}
Both repositories focus on efficient text processing, but llama.cpp is specifically designed for running large language models, while vtm appears to be a more general-purpose text manipulation tool. The code snippets show similar initialization patterns, with llama.cpp using a gpt_params structure and vtm using a vtm_config structure for configuration.
Inference Llama 2 in one file of pure C
Pros of llama2.c
- Focused on implementing the Llama 2 language model in C, offering a lightweight and efficient solution
- Provides a clear and concise implementation, making it easier for developers to understand and modify
- Includes tools for quantization and inference, enhancing performance on resource-constrained devices
Cons of llama2.c
- Limited scope compared to vtm, which offers a broader range of features for text-based user interfaces
- May require more setup and configuration for specific use cases, as it's primarily focused on the Llama 2 model
- Less suitable for creating interactive terminal applications or text-based UIs
Code Comparison
llama2.c:
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
// Initialize the Llama model
Llama* llama = llama_init("path/to/model.bin");
// Generate text
char* output = llama_generate(llama, "Hello, world!");
printf("%s\n", output);
llama_free(llama);
return 0;
}
vtm:
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
// Initialize the VTM screen
VTM_Screen* screen = vtm_screen_new();
// Draw text on the screen
vtm_screen_draw_text(screen, 0, 0, "Hello, world!");
vtm_screen_refresh(screen);
vtm_screen_free(screen);
return 0;
}
This comparison highlights the different focus areas of the two projects, with llama2.c centered on language model implementation and vtm on text-based user interface creation.
Python bindings for llama.cpp
Pros of llama-cpp-python
- Provides Python bindings for the llama.cpp library, enabling easy integration of LLaMA models in Python projects
- Supports various LLaMA model sizes and configurations
- Includes GPU acceleration support for faster inference
Cons of llama-cpp-python
- Limited to LLaMA models, while vtm supports multiple model architectures
- Requires separate installation of llama.cpp and its dependencies
- May have higher memory requirements compared to vtm's optimized implementation
Code Comparison
llama-cpp-python:
from llama_cpp import Llama
llm = Llama(model_path="./models/7B/ggml-model.bin")
output = llm("Q: Name the planets in the solar system? A: ", max_tokens=32, stop=["Q:", "\n"], echo=True)
print(output)
vtm:
from vtm import VTM
model = VTM.from_pretrained("gpt2")
output = model.generate("Name the planets in the solar system:", max_length=50)
print(output)
Summary
llama-cpp-python focuses on providing Python bindings for LLaMA models, offering GPU acceleration and support for various model sizes. However, it's limited to LLaMA architecture and may have higher resource requirements. vtm, on the other hand, supports multiple model architectures and provides a more optimized implementation, but may lack some of the specific features tailored for LLaMA models.
Inference code for Llama models
Pros of Llama
- Developed by Meta, benefiting from extensive resources and research
- Designed for large-scale language modeling tasks
- Supports multiple languages and has a wide range of applications
Cons of Llama
- Requires significant computational resources to run effectively
- May have limitations in specialized or domain-specific tasks
- Potential ethical concerns due to its powerful language generation capabilities
Code Comparison
VTM:
void vtm_init(struct vtm *v) {
v->state = VTM_STATE_INIT;
v->cursor_x = 0;
v->cursor_y = 0;
}
Llama:
def initialize_model(model_path):
model = LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path)
tokenizer = LlamaTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path)
return model, tokenizer
Summary
VTM is a lightweight terminal emulator focused on efficiency and simplicity, while Llama is a powerful large language model designed for complex natural language processing tasks. VTM is more suitable for specific terminal-related applications, whereas Llama excels in general-purpose language understanding and generation across various domains.
The definitive Web UI for local AI, with powerful features and easy setup.
Pros of text-generation-webui
- More comprehensive UI with chat, notebook, and training interfaces
- Supports a wider range of models and architectures
- Active community with frequent updates and contributions
Cons of text-generation-webui
- Higher system requirements due to its extensive features
- Steeper learning curve for new users
- More complex setup process compared to vtm
Code Comparison
text-generation-webui:
def generate_reply(
question, state, stopping_strings=None, is_chat=False, escape_html=False
):
# Complex generation logic with multiple parameters
# ...
vtm:
def generate(self, prompt, max_new_tokens=20):
# Simple generation function with fewer parameters
# ...
The code comparison shows that text-generation-webui offers more advanced generation options, while vtm provides a simpler interface for basic text generation tasks. text-generation-webui's code reflects its broader feature set and flexibility, whereas vtm focuses on a more streamlined approach to text generation.
GPT4All: Run Local LLMs on Any Device. Open-source and available for commercial use.
Pros of gpt4all
- Larger community and more active development (7.8k stars vs 13 for vtm)
- Focuses on providing a local, privacy-friendly AI model
- Offers both command-line and GUI interfaces for ease of use
Cons of gpt4all
- Requires more computational resources due to its large language model
- May have a steeper learning curve for users unfamiliar with AI models
- Less specialized than vtm, which focuses specifically on terminal management
Code Comparison
gpt4all (Python):
from gpt4all import GPT4All
model = GPT4All("ggml-gpt4all-j-v1.3-groovy")
output = model.generate("Once upon a time, ", max_tokens=50)
print(output)
vtm (C):
#include "vtm.h"
int main() {
vtm_init();
vtm_create_window("My Window", 800, 600);
vtm_run();
return 0;
}
The code snippets highlight the different focus areas of the projects. gpt4all is centered around generating text using AI models, while vtm provides terminal management functionality.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
vtm (Virtual Terminal Multiplexer)
Vtm is a text-based application that introduces a new class of Hybrid TUI (HTUI) software, offering a unified experience within a single executable file, whether running in a native graphical window or any standard text console. It can wrap any console application and be nested indefinitely, forming a text-based desktop environment, bridging the gap between traditional TUI and GUI.
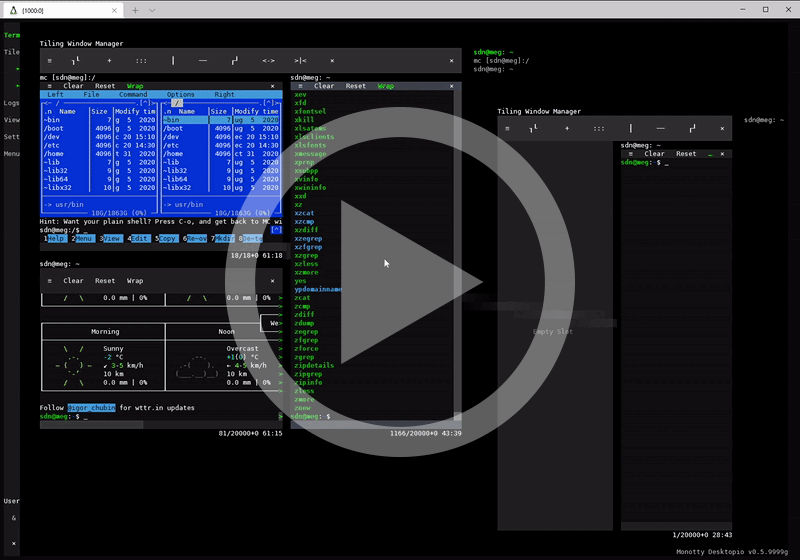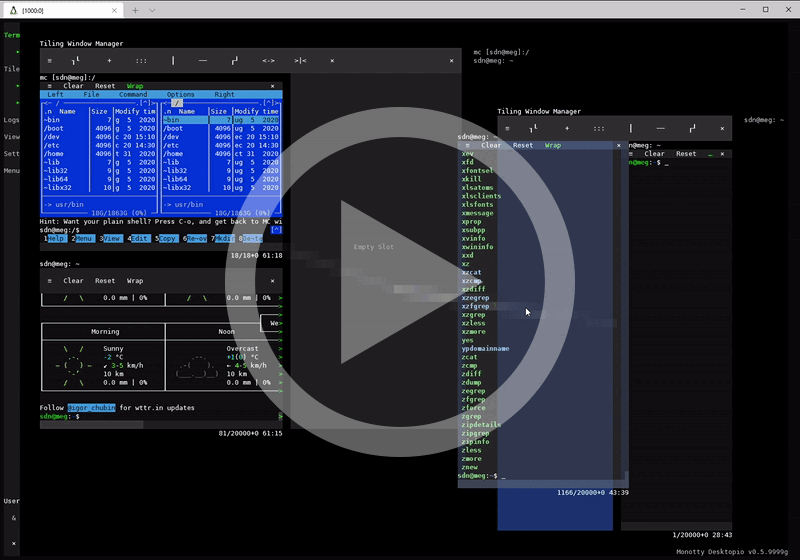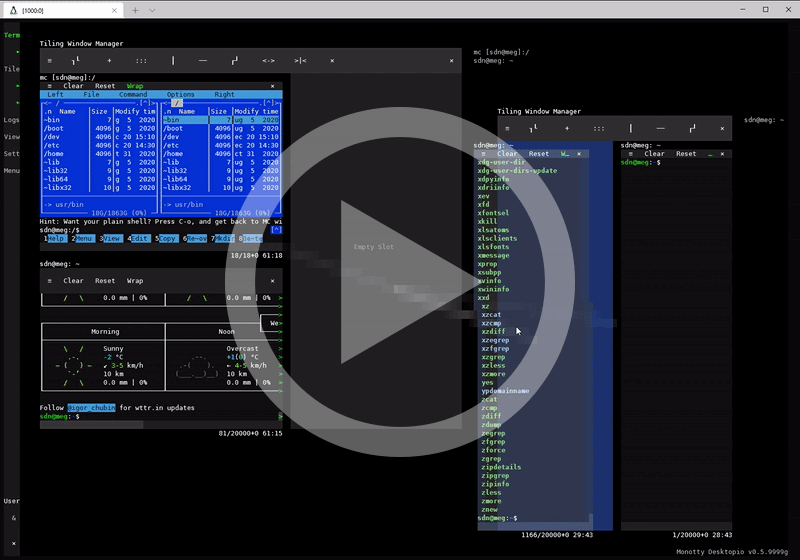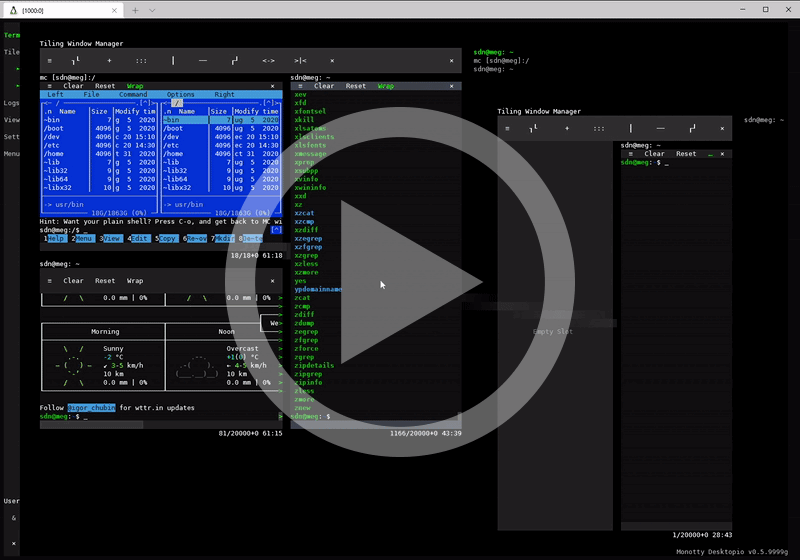
Key features & benefits
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Hybrid TUI (HTUI) | Run the same application seamlessly in both dedicated GUI windows and standard terminals. (GUI mode is available on Windows only for now) |
| Advanced Input | Track all key events, high-resolution mouse movement and window states. |
| VT2D Technology | Scaling and transformation of individual characters or their parts at the cell level. |
| DirectVT I/O | Ability to fully binary serialize/deserialize user input and own visual state through duplex channels (sockets, pipes, SSH-tunnels, TCP-connections, etc.). |
| Desktop Mode | A borderless workspace that allows infinite panning in all directions. |
| Tiling Window Manager | Vtm in desktop mode includes a built-in Tiling Window Manager for organizing the workspace into non-overlapping panels with Drag & Drop support. |
| Multi-User Sessions | Share vtm desktop over a LAN (using inetd, netcat, or SSH). |
| Scripting & UI | Build reactive, scriptable UIs using DynamicXML+Lua. |
| Terminal Mode | A standalone terminal emulator as a wrapper for any console applications for seamless integration with the text-based desktop. |
| Horizontal Scrolling | Support for displaying simultaneously wrapped and non-wrapped text runs in the terminal with horizontal scrolling. |
| Windows Console Server | In-process Windows Console Server own implementation on Windows and independence from conhost.exe. |
Get started
Desktop mode
Run vtm to start the desktop environment.
Terminal mode
Run vtm -r term [<your_shell>] to use vtm as a full-fledged standalone terminal emulator.
Try auto-DirectVT via SSH
Accessing vtm via SSH with auto-DirectVT mode outperforms the classic connection:
vtm ssh user@host vtm
Demos
Check out VT2D power (Windows only for now):
vtm --run test
Hybrid TUI app examples (just concepts):
vtm --run calc
vtm --run text
vtm --run gems
Supported platforms
- Windows
- Windows 8.1 and later (including Windows Server Core and Windows PE)
- Unix-like
- Linux
- macOS
- FreeBSD
- NetBSD
- OpenBSD
...
Currently, rendering into a native GUI window is only available on the Windows platform; on Unix-like platforms, a terminal emulator is required.
Binary downloads
Documentation
Top Related Projects
LLM inference in C/C++
Inference Llama 2 in one file of pure C
Python bindings for llama.cpp
Inference code for Llama models
The definitive Web UI for local AI, with powerful features and easy setup.
GPT4All: Run Local LLMs on Any Device. Open-source and available for commercial use.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot