scalene
scalene
Scalene: a high-performance, high-precision CPU, GPU, and memory profiler for Python with AI-powered optimization proposals
Top Related Projects
Continuous Profiling Platform. Debug performance issues down to a single line of code
Sampling profiler for Python programs
🚴 Call stack profiler for Python. Shows you why your code is slow!
Monitor Memory usage of Python code
Quick Overview
Scalene is a high-performance CPU, GPU, and memory profiler for Python that does not require code changes. It uses sampling instead of instrumentation or relying on Python's tracing facilities, making it both accurate and fast. Scalene provides line-by-line profiling information and can also report memory leaks.
Pros
- High-performance profiling with minimal overhead
- Provides detailed line-by-line profiling for CPU, GPU, and memory usage
- Can detect and report memory leaks
- Works with unmodified Python code
Cons
- May require some setup and configuration for optimal use
- Limited to Python programs (not suitable for other languages)
- Learning curve for interpreting detailed profiling results
- Some features may require specific hardware or system configurations
Code Examples
- Basic usage:
from scalene import scalene_profiler
@scalene_profiler
def my_function():
# Your code here
pass
my_function()
- Profiling a script:
python -m scalene your_script.py
- Generating a profile report:
import scalene
scalene.start()
# Your code here
scalene.stop()
scalene.report()
Getting Started
-
Install Scalene:
pip install scalene -
Profile your Python script:
python -m scalene your_script.py -
View the profiling results in the console or generated HTML report.
-
For more advanced usage, refer to the Scalene documentation for configuration options and API usage.
Competitor Comparisons
Continuous Profiling Platform. Debug performance issues down to a single line of code
Pros of Pyroscope
- Supports multiple programming languages, not just Python
- Offers a web-based UI for visualizing profiling data
- Provides continuous profiling capabilities for production environments
Cons of Pyroscope
- May have higher overhead compared to Scalene's low-overhead profiling
- Requires setting up a separate server for data collection and visualization
- Less focused on memory profiling compared to Scalene's detailed memory analysis
Code Comparison
Scalene usage:
import scalene
scalene.start()
# Your code here
scalene.stop()
Pyroscope usage:
from pyroscope import configure
configure(application_name="my_app", server_address="http://pyroscope:4040")
# Your code here
Both tools aim to provide profiling capabilities, but Pyroscope focuses on continuous profiling across multiple languages, while Scalene specializes in low-overhead Python profiling with detailed CPU and memory analysis. Pyroscope offers a more comprehensive solution for production environments, while Scalene excels in providing precise, low-impact profiling for Python applications during development and testing phases.
Sampling profiler for Python programs
Pros of py-spy
- Written in Rust, offering low overhead and minimal performance impact
- Can attach to running processes without modifying the target program
- Supports profiling of multi-threaded Python applications
Cons of py-spy
- Limited to sampling-based profiling, which may miss short-lived events
- Does not provide memory profiling or allocation tracking
- Less detailed output compared to Scalene's comprehensive reports
Code Comparison
py-spy:
py-spy record -o profile.svg -- python your_script.py
Scalene:
python -m scalene your_script.py
Key Differences
- Scalene provides more detailed profiling, including CPU, memory, and I/O usage
- py-spy is better suited for quick, low-overhead profiling of running processes
- Scalene offers a web-based interface for result visualization, while py-spy typically generates SVG flame graphs
- py-spy can profile Python extensions written in C/C++, which Scalene may struggle with
Both tools have their strengths, with py-spy excelling in simplicity and low overhead, while Scalene offers more comprehensive profiling capabilities at the cost of slightly higher complexity and overhead.
🚴 Call stack profiler for Python. Shows you why your code is slow!
Pros of pyinstrument
- Simpler setup and usage, requiring minimal code changes
- Provides an interactive HTML visualization of the call stack
- Lightweight and has minimal impact on program execution speed
Cons of pyinstrument
- Less detailed memory profiling capabilities
- May not be as accurate for very short-running programs
- Limited support for profiling multi-threaded applications
Code Comparison
pyinstrument:
from pyinstrument import Profiler
profiler = Profiler()
profiler.start()
# Your code here
profiler.stop()
print(profiler.output_text())
Scalene:
import scalene
scalene.start()
# Your code here
scalene.stop()
Both pyinstrument and Scalene are Python profiling tools, but they have different strengths and use cases. pyinstrument is easier to set up and use, providing a simple way to visualize the call stack and identify performance bottlenecks. It's particularly useful for quick profiling tasks and generating easy-to-understand reports.
Scalene, on the other hand, offers more comprehensive profiling, including detailed memory usage analysis and support for multi-threaded applications. It provides more accurate results for short-running programs and offers a wider range of profiling options.
The choice between the two depends on the specific needs of your project, with pyinstrument being better for quick, simple profiling tasks, and Scalene being more suitable for in-depth performance analysis, especially when memory usage is a concern.
Monitor Memory usage of Python code
Pros of memory_profiler
- Simple and lightweight, easy to integrate into existing projects
- Line-by-line memory usage analysis
- Can be used as a Python module or command-line tool
Cons of memory_profiler
- Limited to memory profiling only, doesn't provide CPU or other performance metrics
- May introduce significant overhead, especially for large programs
- Less detailed output compared to Scalene
Code Comparison
memory_profiler:
from memory_profiler import profile
@profile
def my_func():
a = [1] * (10 ** 6)
b = [2] * (2 * 10 ** 7)
del b
return a
Scalene:
# No code changes required
# Run with: scalene your_script.py
Scalene doesn't require code modifications, as it's typically run as a command-line tool. memory_profiler, on the other hand, requires decorating functions or using it as a context manager for profiling specific code blocks.
Both tools serve different purposes: memory_profiler focuses solely on memory usage, while Scalene provides a more comprehensive profiling solution, including CPU, memory, and GPU usage. The choice between them depends on the specific profiling needs of your project.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
![]()
Scalene: a Python CPU+GPU+memory profiler with AI-powered optimization proposals
by Emery Berger, Sam Stern, and Juan Altmayer Pizzorno.

(tweet from Ian Ozsvald, author of High Performance Python)

Python Profiler Links to AI to Improve Code Scalene identifies inefficiencies and asks GPT-4 for suggestions, IEEE Spectrum
Episode 172: Measuring Multiple Facets of Python Performance With Scalene, The Real Python podcast
Scalene web-based user interface: https://scalene-gui.github.io/scalene-gui/
About Scalene
Scalene is a high-performance CPU, GPU and memory profiler for Python that does a number of things that other Python profilers do not and cannot do. It runs orders of magnitude faster than many other profilers while delivering far more detailed information. It is also the first profiler ever to incorporate AI-powered proposed optimizations.
AI-powered optimization suggestions
Note
For optimization suggestions, Scalene supports a variety of AI providers, including Amazon Bedrock, Microsoft Azure, OpenAI, and local models via Ollama. To enable AI-powered optimization suggestions from AI providers, you need to select a provider and, if needed, enter your credentials, in the box under "AI Optimization Options".

Once you've entered your key and any other needed data, click on the lightning bolt (â¡) beside any line or the explosion (ð¥) for an entire region of code to generate a proposed optimization. Click on a proposed optimization to copy it to the clipboard.
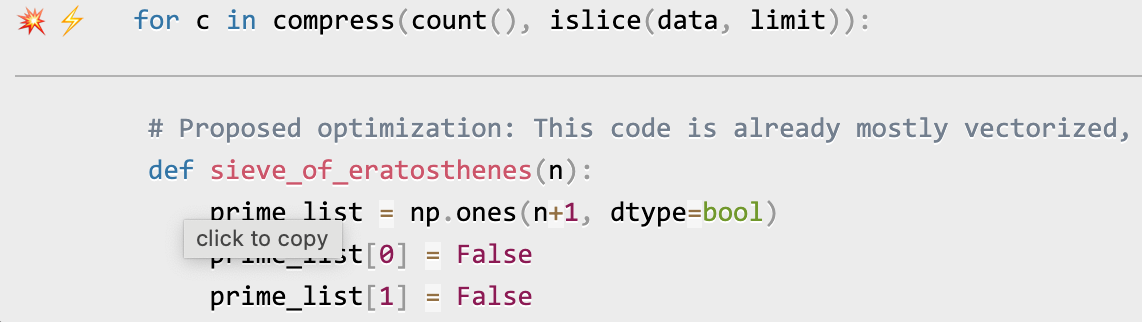
You can click as many times as you like on the lightning bolt or explosion, and it will generate different suggested optimizations. Your mileage may vary, but in some cases, the suggestions are quite impressive (e.g., order-of-magnitude improvements).
Quick Start
Installing Scalene:
python3 -m pip install -U scalene
or
conda install -c conda-forge scalene
Using Scalene:
After installing Scalene, you can use Scalene at the command line, or as a Visual Studio Code extension.
Using the Scalene VS Code Extension:
First, install the Scalene extension from the VS Code Marketplace or by searching for it within VS Code by typing Command-Shift-X (Mac) or Ctrl-Shift-X (Windows). Once that's installed, click Command-Shift-P or Ctrl-Shift-P to open the Command Palette. Then select "Scalene: AI-powered profiling..." (you can start typing Scalene and it will pop up if it's installed). Run that and, assuming your code runs for at least a second, a Scalene profile will appear in a webview.
Commonly used command-line options:
Scalene uses a verb-based command structure with two main commands: run (to profile) and view (to display results).
# Profile a program (saves to scalene-profile.json)
scalene run your_prog.py
python3 -m scalene run your_prog.py # equivalent alternative
# View a profile
scalene view # open profile in browser
scalene view --cli # view in terminal
scalene view --html # save to scalene-profile.html
scalene view --standalone # save as self-contained HTML
# Common profiling options
scalene run --cpu-only your_prog.py # only profile CPU (faster)
scalene run -o results.json your_prog.py # custom output filename
scalene run -c config.yaml your_prog.py # load options from config file
# Pass arguments to your program (use --- separator)
scalene run your_prog.py --- --arg1 --arg2
# Get help
scalene --help # main help
scalene run --help # profiling options
scalene run --help-advanced # advanced profiling options
scalene view --help # viewing options
Using a YAML configuration file:
You can store Scalene options in a YAML configuration file and load them with -c or --config:
scalene run -c scalene.yaml your_prog.py
Example scalene.yaml:
# Output options
outfile: my-profile.json
# Profiling mode (use only one)
cpu-only: true # CPU profiling only (faster)
# gpu: true # Include GPU profiling
# memory: true # Include memory profiling
# Filter what gets profiled
profile-only: "mypackage,mymodule" # Only profile these paths
profile-exclude: "tests,venv" # Exclude these paths
profile-all: false # Profile all code, not just target
# Performance tuning
cpu-percent-threshold: 1 # Min CPU% to report (default: 1)
cpu-sampling-rate: 0.01 # Sampling interval in seconds
malloc-threshold: 100 # Min allocations to report
# Other options
use-virtual-time: false # Measure CPU time only (not I/O)
stacks: false # Collect stack traces
memory-leak-detector: true # Detect likely memory leaks
Command-line arguments override config file settings.
Using Scalene programmatically in your code:
Invoke using scalene as above and then:
from scalene import scalene_profiler
# Turn profiling on
scalene_profiler.start()
# your code
# Turn profiling off
scalene_profiler.stop()
from scalene.scalene_profiler import enable_profiling
with enable_profiling():
# do something
Using Scalene to profile only specific functions via @profile:
Just preface any functions you want to profile with the @profile decorator and run it with Scalene:
# do not import profile!
@profile
def slow_function():
import time
time.sleep(3)
Web-based GUI
Scalene has both a CLI and a web-based GUI (demo here).
By default, once Scalene has profiled your program, it will open a tab in a web browser with an interactive user interface (all processing is done locally). Hover over bars to see breakdowns of CPU and memory consumption, and click on underlined column headers to sort the columns. The GUI works fully offline with no internet connection required.
Use scalene view --standalone to generate a completely self-contained HTML file with all assets embedded, perfect for sharing or archiving.
Scalene Overview
Scalene talk (PyCon US 2021)
This talk presented at PyCon 2021 walks through Scalene's advantages and how to use it to debug the performance of an application (and provides some technical details on its internals). We highly recommend watching this video!
Fast and Accurate
-
Scalene is fast. It uses sampling instead of instrumentation or relying on Python's tracing facilities. Its overhead is typically no more than 10-20% (and often less).
-
Scalene is accurate. We tested CPU profiler accuracy and found that Scalene is among the most accurate profilers, correctly measuring time taken.

- Scalene performs profiling at the line level and per function, pointing to the functions and the specific lines of code responsible for the execution time in your program.
CPU profiling
- Scalene separates out time spent in Python from time in native code (including libraries). Most Python programmers aren't going to optimize the performance of native code (which is usually either in the Python implementation or external libraries), so this helps developers focus their optimization efforts on the code they can actually improve.
- Scalene highlights hotspots (code accounting for significant percentages of CPU time or memory allocation) in red, making them even easier to spot.
- Scalene also separates out system time, making it easy to find I/O bottlenecks.
GPU profiling
- Scalene reports GPU time (currently limited to NVIDIA-based systems).
Memory profiling
- Scalene profiles memory usage. In addition to tracking CPU usage, Scalene also points to the specific lines of code responsible for memory growth. It accomplishes this via an included specialized memory allocator.
- Scalene separates out the percentage of memory consumed by Python code vs. native code.
- Scalene produces per-line memory profiles.
- Scalene identifies lines with likely memory leaks.
- Scalene profiles copying volume, making it easy to spot inadvertent copying, especially due to crossing Python/library boundaries (e.g., accidentally converting
numpyarrays into Python arrays, and vice versa).
Other features
- Scalene can produce reduced profiles (via
--reduced-profile) that only report lines that consume more than 1% of CPU or perform at least 100 allocations. - Scalene supports
@profiledecorators to profile only specific functions. - When Scalene is profiling a program launched in the background (via
&), you can suspend and resume profiling.
Comparison to Other Profilers
Performance and Features
Below is a table comparing the performance and features of various profilers to Scalene.
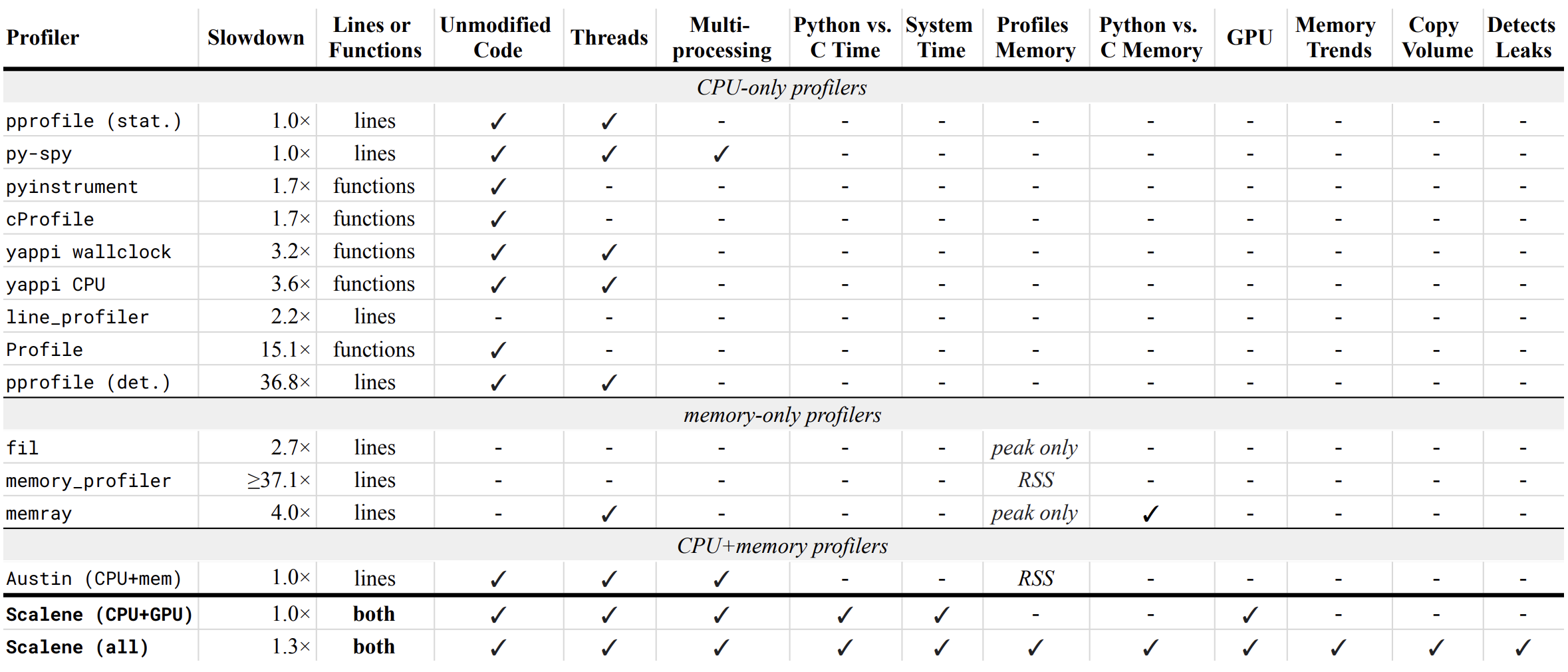
- Slowdown: the slowdown when running a benchmark from the Pyperformance suite. Green means less than 2x overhead. Scalene's overhead is just a 35% slowdown.
Scalene has all of the following features, many of which only Scalene supports:
- Lines or functions: does the profiler report information only for entire functions, or for every line -- Scalene does both.
- Unmodified Code: works on unmodified code.
- Threads: supports Python threads.
- Multiprocessing: supports use of the
multiprocessinglibrary -- Scalene only - Python vs. C time: breaks out time spent in Python vs. native code (e.g., libraries) -- Scalene only
- System time: breaks out system time (e.g., sleeping or performing I/O) -- Scalene only
- Profiles memory: reports memory consumption per line / function
- GPU: reports time spent on an NVIDIA GPU (if present) -- Scalene only
- Memory trends: reports memory use over time per line / function -- Scalene only
- Copy volume: reports megabytes being copied per second -- Scalene only
- Detects leaks: automatically pinpoints lines responsible for likely memory leaks -- Scalene only
Output
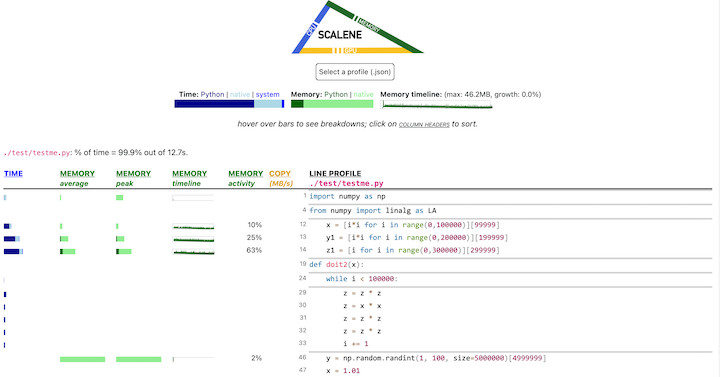
If you include the --cli option, Scalene prints annotated source code for the program being profiled
(as text, JSON (--json), or HTML (--html)) and any modules it
uses in the same directory or subdirectories (you can optionally have
it --profile-all and only include files with at least a
--cpu-percent-threshold of time). Here is a snippet from
pystone.py.
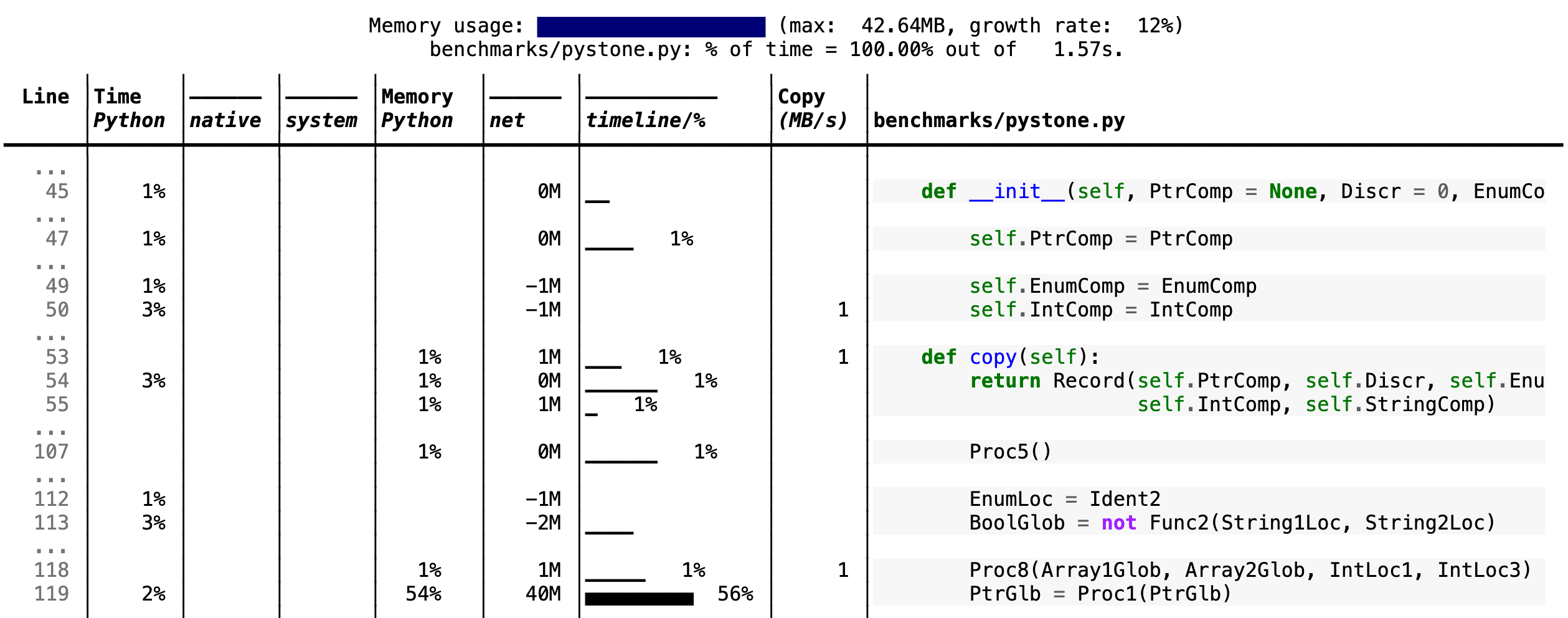
- Memory usage at the top: Visualized by "sparklines", memory consumption over the runtime of the profiled code.
- "Time Python": How much time was spent in Python code.
- "native": How much time was spent in non-Python code (e.g., libraries written in C/C++).
- "system": How much time was spent in the system (e.g., I/O).
- "GPU": (not shown here) How much time spent on the GPU, if your system has an NVIDIA GPU installed.
- "Memory Python": How much of the memory allocation happened on the Python side of the code, as opposed to in non-Python code (e.g., libraries written in C/C++).
- "net": Positive net memory numbers indicate total memory allocation in megabytes; negative net memory numbers indicate memory reclamation.
- "timeline / %": Visualized by "sparklines", memory consumption generated by this line over the program runtime, and the percentages of total memory activity this line represents.
- "Copy (MB/s)": The amount of megabytes being copied per second (see "About Scalene").
Scalene
The following command runs Scalene on a provided example program.
scalene test/testme.py
Click to see all Scalene's options (available by running with --help)
% scalene --help
Scalene: a high-precision CPU and memory profiler, version 1.5.51 (2025.01.29)
https://github.com/plasma-umass/scalene
commands:
run Profile a Python program (saves to scalene-profile.json)
view View an existing profile in browser or terminal
examples:
% scalene run your_program.py # profile, save to scalene-profile.json
% scalene view # view scalene-profile.json in browser
% scalene view --cli # view profile in terminal
in Jupyter, line mode:
%scrun [options] statement
in Jupyter, cell mode:
%%scalene [options]
your code here
% scalene run --help
Profile a Python program with Scalene.
examples:
% scalene run prog.py # profile, save to scalene-profile.json
% scalene run -o my.json prog.py # save to custom file
% scalene run --cpu-only prog.py # profile CPU only (faster)
% scalene run -c scalene.yaml prog.py # load options from config file
% scalene run prog.py --- --arg # pass args to program
% scalene run --help-advanced # show advanced options
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-o, --outfile OUTFILE output file (default: scalene-profile.json)
--cpu-only only profile CPU time (no memory/GPU)
-c, --config FILE load options from YAML config file
--help-advanced show advanced options
% scalene run --help-advanced
Advanced options for scalene run:
background profiling:
Use --off to start with profiling disabled, then control it from another terminal:
% scalene run --off prog.py # start with profiling off
% python3 -m scalene.profile --on --pid <PID> # resume profiling
% python3 -m scalene.profile --off --pid <PID> # suspend profiling
options:
--profile-all profile all code, not just the target program
--profile-only PATH only profile files containing these strings (comma-separated)
--profile-exclude PATH exclude files containing these strings (comma-separated)
--profile-system-libraries profile Python stdlib and installed packages (default: skip)
--gpu profile GPU time and memory
--memory profile memory usage
--stacks collect stack traces
--profile-interval N output profiles every N seconds (default: inf)
--use-virtual-time measure only CPU time, not I/O or blocking
--cpu-percent-threshold N only report lines with at least N% CPU (default: 1%)
--cpu-sampling-rate N CPU sampling rate in seconds (default: 0.01)
--allocation-sampling-window N allocation sampling window in bytes
--malloc-threshold N only report lines with at least N allocations (default: 100)
--program-path PATH directory containing code to profile
--memory-leak-detector EXPERIMENTAL: report likely memory leaks
--on start with profiling on (default)
--off start with profiling off
% scalene view --help
View an existing Scalene profile.
examples:
% scalene view # open in browser
% scalene view --cli # view in terminal
% scalene view --html # save to scalene-profile.html
% scalene view --standalone # save as self-contained HTML
% scalene view myprofile.json # open specific profile in browser
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--cli display profile in the terminal
--html save to scalene-profile.html (no browser)
--standalone save as self-contained HTML with all assets embedded
-r, --reduced only show lines with activity (--cli mode)
Scalene with Jupyter
Instructions for installing and using Scalene with Jupyter notebooks
This notebook illustrates the use of Scalene in Jupyter.
Installation:
!pip install scalene
%load_ext scalene
Line mode:
%scrun [options] statement
Cell mode:
%%scalene [options]
code...
code...
Installation
Using pip (Mac OS X, Linux, Windows, and WSL2)
Scalene is distributed as a pip package and works on Mac OS X, Linux (including Ubuntu in Windows WSL2) and Windows platforms.
Note for Windows users
Starting with Scalene 2.0, Windows supports full memory profiling. If you encounter issues, ensure you have the Visual C++ Redistributable installed. If building from source, you will need Visual C++ Build Tools and CMake.
You can install it as follows:
% pip install -U scalene
or
% python3 -m pip install -U scalene
You may need to install some packages first.
See https://stackoverflow.com/a/19344978/4954434 for full instructions for all Linux flavors.
For Ubuntu/Debian:
% sudo apt install git python3-all-dev
Using conda (Mac OS X, Linux, Windows, and WSL2)
% conda install -c conda-forge scalene
Scalene is distributed as a conda package and works on Mac OS X, Linux (including Ubuntu in Windows WSL2) and Windows platforms.
Note for Windows users
Starting with Scalene 2.0, Windows supports full memory profiling. If you encounter issues, ensure you have the Visual C++ Redistributable installed.
On ArchLinux
You can install Scalene on Arch Linux via the AUR
package. Use your favorite AUR helper, or
manually download the PKGBUILD and run makepkg -cirs to build. Note that this will place
libscalene.so in /usr/lib; modify the below usage instructions accordingly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use Scalene with PyTest?
A: Yes! You can run it as follows (for example):
scalene run -m pytest your_test.py
or
python3 -m scalene run -m pytest your_test.py
Is there any way to get shorter profiles or do more targeted profiling?
A: Yes! There are several options:
- Use
--reduced-profileto include only lines and files with memory/CPU/GPU activity. - Use
--profile-onlyto include only filenames containing specific strings (as in,--profile-only foo,bar,baz). - Decorate functions of interest with
@profileto have Scalene report only those functions. - Turn profiling on and off programmatically by importing Scalene profiler (
from scalene import scalene_profiler) and then turning profiling on and off viascalene_profiler.start()andscalene_profiler.stop(). By default, Scalene runs with profiling on, so to delay profiling until desired, use the--offcommand-line option (scalene run --off yourprogram.py).
How do I run Scalene in PyCharm?
A: In PyCharm, you can run Scalene at the command line by opening the terminal at the bottom of the IDE and running a Scalene command (e.g., scalene run <your program>). Then use scalene view --html to generate an HTML file (scalene-profile.html) that you can view in the IDE.
How do I use Scalene with Django?
A: Pass in the --noreload option (see https://github.com/plasma-umass/scalene/issues/178).
Does Scalene work with gevent/Greenlets?
A: Yes! Put the following code in the beginning of your program, or modify the call to monkey.patch_all as below:
from gevent import monkey
monkey.patch_all(thread=False)
How do I use Scalene with PyTorch on the Mac?
A: Scalene works with PyTorch version 1.5.1 on Mac OS X. There's a bug in newer versions of PyTorch (https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/57185) that interferes with Scalene (discussion here: https://github.com/plasma-umass/scalene/issues/110), but only on Macs.
Technical Information
For details about how Scalene works, please see the following paper, which won the Jay Lepreau Best Paper Award at OSDI 2023: Triangulating Python Performance Issues with Scalene. (Note that this paper does not include information about the AI-driven proposed optimizations.)
To cite Scalene in an academic paper, please use the following:
@inproceedings{288540,
author = {Emery D. Berger and Sam Stern and Juan Altmayer Pizzorno},
title = {Triangulating Python Performance Issues with {S}calene},
booktitle = {{17th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 23)}},
year = {2023},
isbn = {978-1-939133-34-2},
address = {Boston, MA},
pages = {51--64},
url = {https://www.usenix.org/conference/osdi23/presentation/berger},
publisher = {USENIX Association},
month = jul
}
Success Stories
If you use Scalene to successfully debug a performance problem, please add a comment to this issue!
Acknowledgements
Logo created by Sophia Berger.
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 1955610. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Top Related Projects
Continuous Profiling Platform. Debug performance issues down to a single line of code
Sampling profiler for Python programs
🚴 Call stack profiler for Python. Shows you why your code is slow!
Monitor Memory usage of Python code
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot